Introduction
Images play a crucial role in enhancing the overall user experience of a website. However, they can also impact the website’s ranking and visibility in search engine results. In this digital age, it’s essential to optimize images for search engine optimization (SEO) purposes. This article will provide valuable insights on how to name your images and ensure they contribute to your SEO performance.
What Is Image SEO?
Image SEO is the practice of optimizing images for search engines. The essential factors include captions, alt text, metadata, and optimizing the size and weight of images.
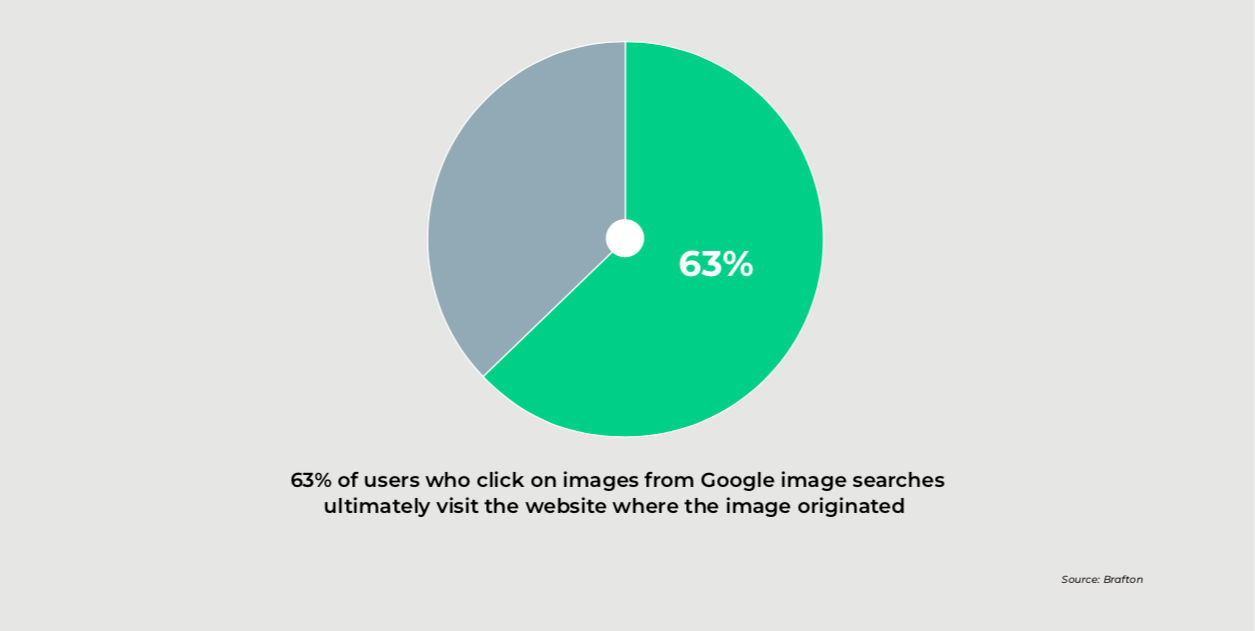
Achieving good image SEO contributes to overall on-page SEO and your page ranking. According to a study by Brafton, 63% of people who click on images on Google end up visiting the website where the image originates.
Chapter 1: 6 Benefits of SEO-Optimized Images
Image SEO, or search engine optimization for images, involves the use of descriptive file names, alt tags, and captions that provide search engines with valuable context about the content. This not only aids in better indexing but also improves accessibility for users with visual impairments, aligning with inclusive web practices. Furthermore, image SEO offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly enhance a website’s visibility and user experience.
1. Better On-Page SEO
Optimized images play a critical role in elevating on-page SEO by enhancing both the user experience and search engine visibility. An efficiently compressed image results in faster page loading times, which is vital for search rankings.
Using descriptive file names, alt tags, and captions provides search engines with the context necessary to boost SEO. If the image is relevant and appealing, visitors will stay on the page, reducing bounce rates and improving the on-page SEO performance.
2. More Traffic Through Image Search
Image SEO facilitates better image search visibility, opening up additional channels for organic traffic. When images are appropriately optimized with descriptive file names, alt tags, and captions, search engines can better understand and index the content. This optimization enhances the chance of images appearing in relevant search results, attracting a broader audience interested in visual content.
As search engines increasingly prioritize images, a well-optimized image portfolio creates more opportunities for visibility and click-throughs, ultimately driving targeted traffic to a website.
3. More Social Sharing
Optimized images significantly enhance social sharing by making content visually appealing and share-worthy. Properly formatted and compressed images load quickly, capturing users’ attention in social media feeds. Descriptive file names and alt tags contribute to better accessibility, ensuring that the image’s intent is clear even without accompanying text. Social media platforms prioritize visually engaging content, and optimized images stand out, prompting higher engagement rates and increased shares.
Additionally, optimized images lead to a more cohesive and attractive overall social media presence, fostering a positive perception of the brand.
4. More Backlinks
Strategic image SEO can be a powerful avenue for increased backlinks. When your images are meticulously optimized, search engines recognize and prioritize your content, attracting a broader audience. Engaged users are more likely to share visually appealing and well-optimized images across platforms, creating a ripple effect of organic backlinks. Harnessing the potential of image SEO not only enhances your website’s visibility, but also establishes credibility, enticing other websites to link back to your content.
5. Better User Experience and Engagement
Optimized images contribute to a more engaging user experience, as visually appealing content tends to capture and retain visitor attention. This can result in increased user dwell time, reduced bounce rates, and higher conversion rates, positively impacting a site’s overall performance.
When a user comes across optimized images, they have a seamless and visually appealing experience. As a result, visitors tend to come back to the site and explore further, which also increases dwell time.
6. Better Web Accessibility
Optimized images play a crucial role in enhancing web accessibility by providing inclusive experiences for all users. Image optimization techniques, such as alt text, simplify navigation for visitors using screen readers. Prioritizing accessibility not only meets ethical standards but also positively influences search engine rankings, demonstrating that image optimization goes beyond aesthetics and fosters a more inclusive and user-friendly web environment.
Chapter 2: Image SEO Optimization Opportunities
Image SEO optimization presents several opportunities to enhance the visibility and performance of images on your website. Here are 14 ways you can optimize your images and improve your SEO:
1. Check the Image Source (Original or Stock):
You can choose to produce original images or rely on stock photography. Both options have advantages and downsides.
- Original photography: One-of-a-kind images, usually photos taken in a studio, or custom created digitally, are of higher quality. On the downside, they’re more expensive to produce and require special equipment, a professional photographer, and editing skills.
- Stock images: These are relatively inexpensive — some are even free — and readily available. The downside is that, depending on the license, other people may be using the same image for their content, and it may be difficult to find the right photo for what you need.
If you choose to use a stock photo, beware of image copyrights. Check what the license allows you to do and what it doesn’t.
2. Page Title, Meta Tags, and Content
Consider your page title. Google uses your page title and description to rank your site and automatically generates a title link. Depending on how effective the title is, users may or may not click on the link.
SEO factors like meta data, header tags, and the content on the page affect how your images rank on Google.
What meta tags should you add? For instance, the title tag is a version of the title of your page optimized for SEO. It should incorporate the main keyword and be no more than 55 characters. Another type of meta tag is an alt tag, which adds text data to images so web crawlers can find them. This helps your image to show up in searches.
Finally, remember that relevant, high-quality content is critical to SEO success. Use relevant keywords naturally throughout your articles.
3. The Image File Format
File type has an impact on SEO, so it’s essential to choose formats and name images deliberately. Certain file types, such as JPEG and PNG, are more search-engine friendly and load faster, positively impacting SEO efforts.
4. Image Filename
Give your image files a name that helps you rank higher in search engines. An SEO-friendly name helps search crawlers scan your webpages, pulling information from the source code to rank your page. Image filenames are part of that information.
How do you choose a good file name for your images? An image filename should be clear and descriptive, and it should tell what the image is about in a few words. If the image is of a red car on a highway, for example, its name should be “red-car-on-highway.jpg.”
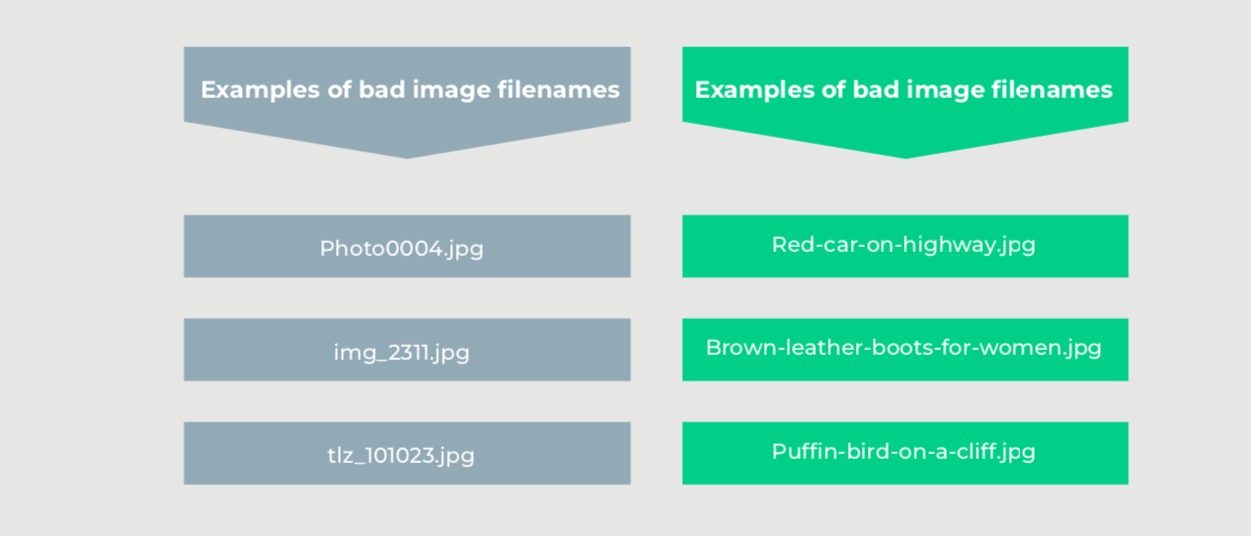
Use keywords wisely. Your file names should be rich in keywords, but avoid keyword stuffing. This provides context to search engines about the image’s content and increases its visibility in relevant search queries.
5. Image File Path
One of the recent updates to Google guidelines is that the file name and path are now ranking factors. If you have the images for your different products stored in a single media folder, you’re missing the opportunity to rank by file path. Instead, create subfolders for each image category, like electronics, sports gear, and so on.
6. Image Alt Text
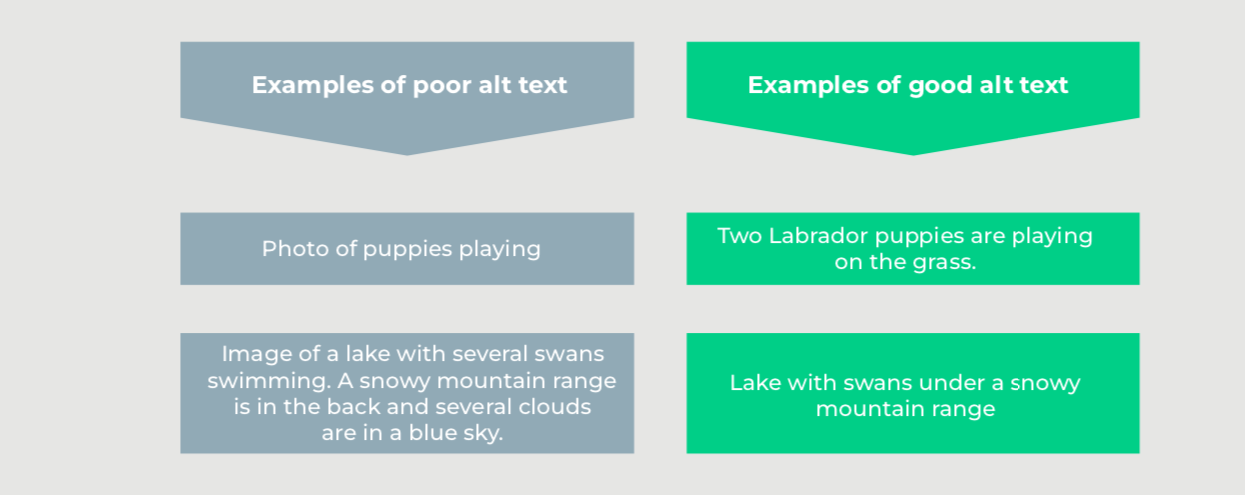
Alt text is short for alternative text. This text describes the content of an image for users who may not see it, such as users who rely on screen readers. Search engines use alt text to understand what an image is about.
How do you write effective alt text for your images?
- Describe what is in the image in detail. The text should tell a reader who doesn’t see the image what is in it.
- Keep it short. The best alt text is under 125 characters to ensure screen readers can process the information quickly.
- Incorporate keywords. This will improve the image’s SEO. However, keep the user experience in mind. Only include keywords that fit naturally and describe what’s in the image. Don’t force keywords into the text.
7. Image Title
Another opportunity comes from optimizing the image title. The image title is the text that provides a name and label for an image. It appears when you hover your cursor over the image.
How do you write a good image title?
- Aim for short and effective. It should describe the image but be engaging; 5–8 words will work.
- The title should represent the image’s content accurately. Use terms that describe the subject, color, quantity, and background.
- Add keywords to the title in a natural way. Be specific, but avoid keyword stuffing.

8. Image Caption
The caption is the text description that appears below the image. The caption gives additional context about the image and helps users understand how it’s related to the surrounding content.
Tips for crafting good captions
- The caption should be a whole sentence with a subject, verb, and object.
- It should clearly explain what’s happening in the image and give details that may not be obvious from the image alone.
- The caption should be related to the topic of your article.
- Don’t forget to include the target keywords in the caption, but avoid keyword stuffing.
Example of a good image caption:

Puffin birds in Midcoast Maine. (Image source)
Example of a bad image caption:

Image of puffins.
9. Image Dimensions
While there is no specific size required for an image to show up on Google, there are different sizing guidelines. Choose according to your SEO goals:
- If you want an article to rank in Google News, your images should be high resolution — the Google recommendation is 50,000 pixels minimum width and height. The images should be in a 1×1 aspect ratio.
- If you want to rank on Google Discover, the images should be larger — at least 1200 pixels wide and maximum size for preview.
10. Image Responsiveness
Let’s face it, most people browse the internet on mobile devices. A responsive image is one that adapts in size and resolution to the screen, regardless of the device. This responsiveness saves the user from having to zoom in on an image or site when browsing on mobile.
While accommodating images to any device width was an extra some years ago, it’s now the standard for the user experience. The goal is to keep the images on your site looking as good on a tablet or mobile phone as they do on a desktop.
How do you optimize your images to be responsive?
- Image optimization for responsiveness happens at the web development stage. Responsive development ensures the website is tailored to different screen sizes.
- Developers create responsive image variants to accommodate desktop, tablet, and mobile devices. Too many variants may negatively impact the caching performance, so sometimes developers choose a limited number of image variants, enough to optimize the image but not so many that caching is affected.
11. Image File Size
Another technique in image SEO is to ensure your images are not only the right dimensions but also compressed. This ensures that the server displays the image at the smallest possible file size without compromising loading times.
Compressing file sizes is important to prevent the image’s weight from slowing down page loading times. However, image compression sometimes affects the image resolution. Some content management platforms, like WordPress, automatically compress the images you upload. This automatic compression is often not enough to prevent damage to the resolution.
You can use tools like JPEGmini, Kraken.io, or ImageOptim to optimize your images without compromising quality.
Example of a compressed image:
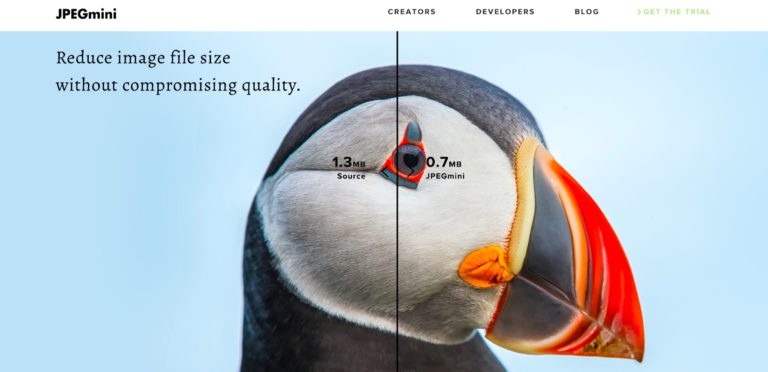
Online tools like JPEGmini can reduce image file size without compromising quality. (Image source)
12. Image Load Time
All these techniques — compressing file size, reducing image dimensions — have the purpose of reducing page load time. Let’s explore why faster load times are important.
When a visitor opens a web page, they expect to see the images at the same time they see the text. Still, sometimes, heavy images may take some time to load, delaying the user from enjoying the page immediately.
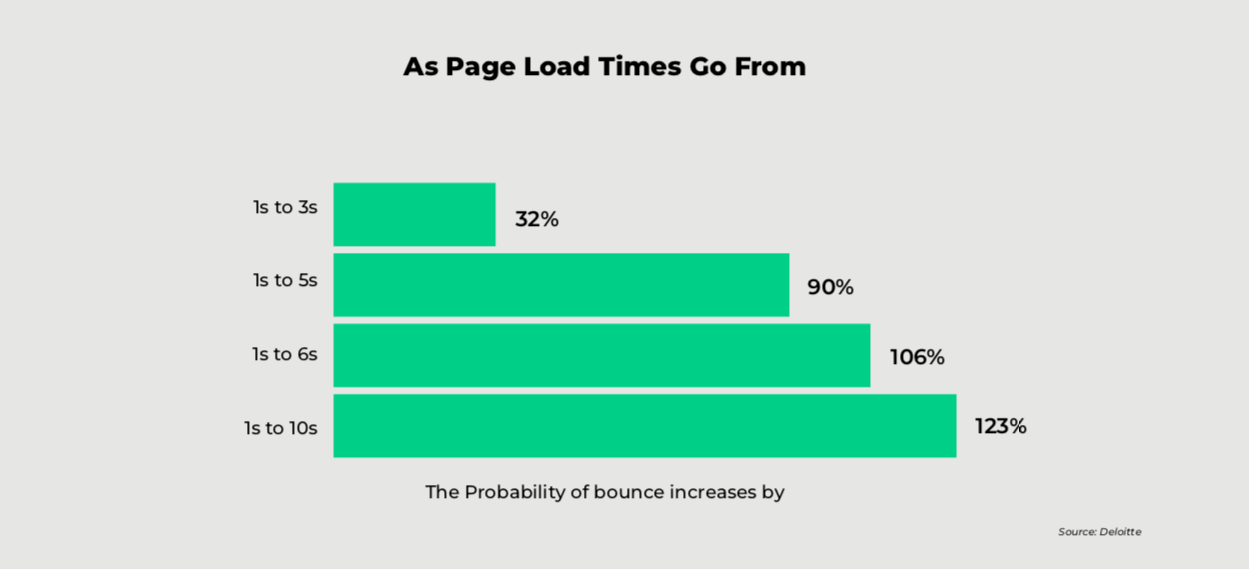
However small, these delays can significantly impact the user experience and the time the user stays on the page. If the page takes too long to load, users may get frustrated and bounce off the site. A 2017 Google study showed that even a 3-second delay can increase bounce rates by 32%. The impact is consistent for both desktop and mobile sites.
Some techniques you can use to speed up image loading times
- Lazy Loading: In this technique, instead of loading every element on the page at once, the browser waits to load the images until they are really needed. Thus, the page loads faster.
- Use a Content Delivery Network: A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a group of servers that caches and delivers content to end users. CDNs cache the browser and reuse previously opened sessions, improving loading times.
13. Image Sitemap
An image sitemap is a type of sitemap that allows search engines to crawl images on a website, therefore enhancing its ranking in search results. A sitemap highlights the important content on a site, helping crawlers discover it.
How does it work? A search engine crawls a website, checking for.txt files, meta data and other information that can help evaluate how relevant the content is to the search query. An XML sitemap lets a website owner set specific information for the crawlers to find, customizing what content is important on the page, including images.
14. Structured Data for Image
To maximize the impact of image optimization, website owners can also utilize structured data markup, such as schema.org, to provide further information to search engines, making the images more searchable. Structured data is organized in a way that’s easy for search engines to read, increasing visibility in search engine result pages and increasing the chances of being featured in rich snippets.
Get the latest growth ideas, strategies, and best practices delivered to your inbox.
Quick read that helps 7000+ subscribers.
Optimized Images Are Key for SEO Positioning
Optimizing images for SEO is not just about keywords and tags — it’s about enhancing the user experience, website performance, and social media visibility. Implement the strategies outlined in this eBook to unlock the full potential of your visual content and boost your online presence. Your website’s success depends on it.
Learn how LeadsPanda can help with your content needs.



